Recent AI Advancements Could Turbocharge the Robotics Sector
Recent advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) have boosted the prospects of many business sectors, but the robotics industry could ultimately be one of the biggest beneficiaries

- Recent advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) are expected to electrify the potential of the robotics industry.
- One of the top-performers in the robotics industry in 2023—Symbotic (SYM)—has successfully integrated AI with robotics as part of its warehousing logistics platform.
- Shares in Symbotic are up more than 200%, while two of the best-known robotics ETFs—Global X Robotics & Artificial Intelligence ETF (BOTZ) and the ROBO Global Robotics & Automation Index ETF (ROBO)—are up 12% and 7%, respectively, in 2023.
It’s still the early innings, but recent developments in the field of artificial intelligence (AI) have begun to fulfill some of the sector’s longtime promise.
ChatGPT has been so popular that most estimates indicate it’s the fastest growing application in history. Moreover, the skyrocketing valuation of ChatGPT’s parent—OpenAI—illustrates how the longtime potential of artificial intelligence has become today’s reality.
Considering the complexities of this particular niche, it’s hard to imagine where AI goes from here, but it’s not hard to imagine that recent AI advancements will electrify the potential of the robotics industry.
Science fiction has long captivated millions of fans worldwide, and now one of the main concepts from the world of sci-fi—AI-powered robots—could soon be a reality. In the not-too-distant future, a real-life robot from Star Wars—such as R2-D2 or C-3PO—may be giving tours at Hollywood Studios.
Looking further into the future, it’s easy to imagine robots/androids exploring outer space on behalf of humanity, as detailed through the Blade Runner franchise. The rovers currently on Mars represent an early example of this approach.
Considering the incredible potential, it’s entirely possible that the successful marriage of artificial intelligence and robotics could represent one of the greatest technological achievements in the history of human civilization.
That’s because a robot/android equipped with AI can progressively get better at executing tasks. Using a variety of sensors, these robots can collect real-time information, and make real-time adjustments/decisions.
The integration of AI will basically transform robots into “smart” machines that can solve problems as they encounter them. At that point, the robot/android is no longer carrying out a series of predefined instructions, but working to solve problems on its own using what it’s learned from training data, previous experience and trial/error.
Much like the imaginations of those pioneers that originally conceived these “sentient” machines, the possibilities seem limitless.
Millions of Robots are Already Deployed Across Various Industries
These days, most of the advancements in robotics fall beyond the purview of the average person’s awareness. Aside from household robots such as the Roomba, the majority of people are not interacting with robots on a daily basis.
However, that doesn’t mean the sector hasn’t been advancing. Today, it’s estimated that more than a million robots are currently deployed at factories in the global automotive industry.
That’s by far the highest concentration of robots for any single business sector, and represents about one-third of the total number of robots deployed across all industries globally. The image below highlights the countries with the highest ratios of robot workers to human workers in the auto manufacturing sector.
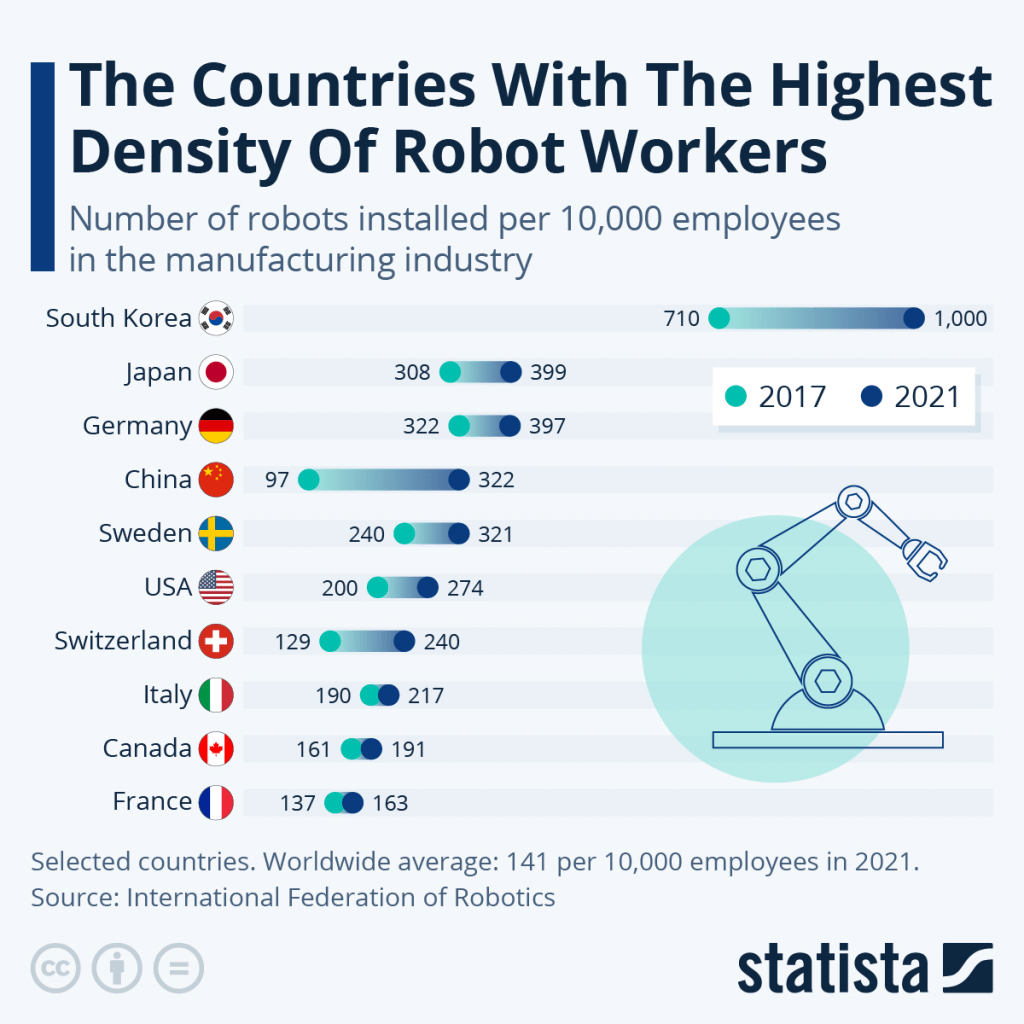
In the automotive industry, the most commonly utilized robot is known as an “articulated robot arm.” These robots are used for a variety of tasks in the manufacturing process, such as assembling, welding and finishing.
In addition to articulated arms, automobile manufacturers also utilize Delta robots, Cartesian robots, cobots and Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arms (known as “SCARA robots”).
Looking beyond the automotive industry, robots are also commonly utilized for other types of industrial manufacturing (electronics, plastics, chemicals), commercial farming and logistics/warehousing. Robots are also commonly found in the medical industry, primarily to assist with surgeries.
Why Symbotic (SYM) Currently Stands Out in the Robotics Industry
The world’s first pure robotics company—Unimation—was founded back in 1962 by Joseph F. Engelberger and George Devol in the United States. Unimation successfully commercialized the earliest robots used in the automotive industry, which were tasked with lifting, stacking, casting and welding.
The first Unimation robots were installed at a General Motors factory in New Jersey during the early 1960s. However, companies such as Chrysler, Ford and Fiat quickly followed suit.
Unimation was ultimately acquired by Westinghouse, which was also an early pioneer in the field. In 1926, engineers at Westinghouse developed the robot “Televox,” which was a telephone-operated industrial switching machine—believed to be one of the earliest robots ever put to commercial use.
According to reports from that period, Televox could “regulate the flow of gas, water or electricity in factories or utility plants by instructing electrical relays to open or close in specific sequences. Before this time, a human switch operator had to be present at each step.”
Today, one of the best-known robotics companies is iRobot (IRBT), which developed the first robot vacuum—the Roomba. The company was founded in 1990 by three members of the MIT Artificial Intelligence Lab. To date, iRobot has sold roughly 30 million home-use robots.
In August of 2022, Amazon (AMZN) announced it would acquire iRobot for $1.7 billion. However, the deal has not yet been cleared by global regulators, and Amazon has since reduced its bid to $1.4 billion.
Some of the other well-known companies operating in the robotics sector are highlighted below (sorted by year-to-date return):
- Symbotic (SYM), +240%
- Nvidia (NVDA), +200%
- Tesla (TSLA), +96%
- PTC Inc. (PTC), +14%
- ABB (ABBNY), +9%
- Stryker Corp (SYK), +7%
- Teradyne (TER), +6%
- Intuitive Surgical (ISRG), +3%
- Rockwell Automation (ROK), +2%
- Emerson Electric (EMR), -6%
- Thermo Fisher Scientific (TMO), -17%
- Zebra Technologies (ZBRA), -21%
- Ambarella (AMBA), -39%
Unfortunately, some of the stocks listed above are large cap companies, and as such, the robotics divisions of these companies only represent a small part of the company’s overall operations. This is definitely true of Tesla, which is developing a robotic humanoid known as “Optimus” (aka the Tesla Bot).
Nvidia is also included on the list because it has developed the most advanced AI chips and software on the market, which makes it a natural partner for any cutting-edge robotics company. Intuitive Surgical represents somewhat of a pure-play on robotics, because the company was an early pioneer of robot-assisted surgeries, and could offer significant future potential if it successfully integrates AI into its products and services.
Of the companies listed above, one of the most intriguing is Symbiotic, which has seen its shares skyrocket in 2023. Symbotic operates in a red-hot niche of robotics—warehouse logistics. Symbotic went public last year via a special purpose acquisition company (SPAC) and has seen its shares rally by roughly 290% since that time.
Taking Stock of Symbotic
Symbotic created an end-to-end warehouse management platform that integrates both AI software and robotics. The company has already sold its platform to retailing giants such as Albertsons (ACI), Target (TGT) and Walmart (WMT), and recently partnered with SoftBank (SFTBY) on a joint venture known as “GreenBox Systems.”
Through this initiative, SoftBank and Symbotic intend to deliver AI-powered logistics and warehousing solutions to smaller companies. Softbank reportedly owns around 8% of Symbotic, and 65% of the GreenBox Systems joint venture.
Walmart also holds a stake in Symotic, which was negotiated when Walmart first agreed to deploy the Symbotic warehousing platform across 42 of its regional distribution centers focused on packaged consumer goods. That stake was recently estimated to represent about 11% of Symbotic, according to a recent proxy statement released by the emerging robotics company.
Symbotic has previously boasted that its platform “enables companies to move goods with unmatched speed, agility, accuracy and efficiency.” Considering the company’s list of existing customers, and the fact that it convinced SoftBank to partner on the GreenBox initiative, the future looks bright for one of the few companies that appears to have already successfully integrated AI with robotics.
The sharp appreciation in the shares of Symbotic since it went public last June also help illustrate the sky-high potential for other companies that successfully commercialize AI-integrated robotics solutions.
For this reason, investors and traders may want to keep a close eye on other robotics companies that go public via a traditional initial public offering (IPO) or SPAC merger in the coming months.
Market participants that prefer exchange-traded funds (ETFs) over single stocks can also consider the Global X Robotics & Artificial Intelligence ETF (BOTZ) and the ROBO Global Robotics & Automation Index ETF (ROBO), which are up 12% and 7%, respectively, in 2023.
To follow everything moving the markets, including the options markets, tune into tastylive—weekdays from 7 a.m. to 4 p.m. CDT.
For daily financial market news and commentary, visit the News & Insights page at tastylive or the YouTube channels tastylive (for options traders), and tastyliveTrending for stocks, futures, forex & macro.
Trade with a better broker, open a tastytrade account today. tastylive, Inc. and tastytrade, Inc. are separate but affiliated companies.
Hungry for more? The next issue of Luckbox is food-focused looking at new growth opportunities and trading ideas in food, beverage, agricultural, hospitality and grocery stocks. Not a subscriber? Subscribe for free at getluckbox.com.